 (not good)
(not good)
Home Page
Pinyin dictionary
An unorthodox course in spoken Chinese: Bending the rules in order to make it easier to study Pinyin
Introduction | Section 1 | Section 2 | Section 3 | Section 4 | Section 5 | Section 6 | Section 7 | Section 8
Example: bu4 hao3  (not good) (not good) |
|
Memory aid: Many of you will remember that Beijing was formerly spelt Peking so as beijing is the spelling in pinyin of Peking the pronunciation of b in beijing is in fact the sound of p. IN THIS SECOND SECTION (and in the next six sections as well) I will be putting the emphasis on the pronunciation in pinyin that is completely different from that in English as this constitutes the main hurdle to the learning of spoken Chinese for English-speaking students. I am referring to the following letters that you should not pronounce as you do in English: b, c, d, g, j, q, x, zh and z as well as the p, t and k sounds which in pinyin are always aspirated (voiced). But if you know their equivalence in English (even if the pedants will tell you that it is not really the same sound), the whole thing becomes quite simple. And yet, you have not really sacrificed much in the sense that you will not be less understood even if it is not 100% the same sound as in English. In this lesson we will just look at how the letter b in pinyin should be pronounced. English-speaking students will need some time and plenty of practice to get used to the fact that in pinyin (i.e. romanized Chinese) the b is not pronounced as the b in bad but rather as the p in pad. So please don't be afraid to pronounce bu as poo (so bu4 hao3 meaning "not good" should be pronounced as "poo4 how3", yes with the tones please)! As a matter of fact you have no choice - you just have to pronounce the b in pinyin as p if you want to be understood. In other words you will have to "unlearn" your English alphabet for b and a few other letters which will be dealt with in the lessons to come. There is no point moving on until this important difference with English has become second nature - which means plenty of practice will be needed. Apart from getting used to pronouncing them according to the pinyin system the words that follow are important to be learnt for their own sake as they constitute commonly-used words and expressions that will eventually have to be learnt if you are to acquire a basic vocabulary of Chinese. Although this lesson is essentially on words starting with the letter b I cannot help bringing in other words and other sounds that have not been dealt with yet but will be dealt with in later lessons. So don't worry too much about these new sounds though you are already meeting them now. Anyway, even if you don't commit them to memory, the fact that you are able to pronounce them correctly (I mean with one of the four tones even if you have to look at the words) is already a first achievement. No mean feat indeed. Just imagine, you have a Chinese man or woman in front of you, you take out your notes (or Chinese book with pinyin) and say what you want to say to him or her by looking at the Chinese word (spelt in pinyin) and pronouncing it with its corresponding tone. I bet you'll be able to do this at the end of this course if not sooner as we go along. So even if you can't read from the written Chinese characters you should be able to produce the same result i.e. communicate what you want to say in Chinese, through pinyin. The most difficult part in learning Chinese is not in the construction of sentences but in being able to pronounce the words in pinyin the Chinese way (I am sorry if I have already said this before but I cannot help emphasizing it). So try to read all these words in pinyin that start with the letter b which should NOT be pronounced as b! Thus Beijing is actually pronounced as "pay_ching"  and not "bayjing" as TV news presenters pronounce it - can't blame them though as they are only pronouncing it the English way. and not "bayjing" as TV news presenters pronounce it - can't blame them though as they are only pronouncing it the English way.
East, south, west, northIn fact the word bei when it carries the third tone bei3  means "north". (Beijing actually means "city to the north"). Anyone who has been to China will tell you that the four directions play a very important role in the day-to-day lives of the Chinese people: names of streets and subway stations contain them and even when you ask for directions you will quite often be told to "Turn to the west" (or east or north or south) instead of "turn right" or "turn left". And, by the way, the Chinese don't learn the four cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) in the same order as we do in English. To them it's dong1 nan2 xi1 bei3 means "north". (Beijing actually means "city to the north"). Anyone who has been to China will tell you that the four directions play a very important role in the day-to-day lives of the Chinese people: names of streets and subway stations contain them and even when you ask for directions you will quite often be told to "Turn to the west" (or east or north or south) instead of "turn right" or "turn left". And, by the way, the Chinese don't learn the four cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) in the same order as we do in English. To them it's dong1 nan2 xi1 bei3  (east, south, west, north) i.e. in clockwise order instead of jumping from one end to the opposite direction as in English. Different cultures, different mores... (east, south, west, north) i.e. in clockwise order instead of jumping from one end to the opposite direction as in English. Different cultures, different mores...
But the same word bei when it carries the first tone i.e. bei1 as in bei1 zi3  means a cup or a glass (to avoid ambiguity you can refer to a glass as bo1 li2 bei1 means a cup or a glass (to avoid ambiguity you can refer to a glass as bo1 li2 bei1  ) )
The word ba1  carrying the first tone means "eight" while in its fourth tone it means daddy (ba4ba carrying the first tone means "eight" while in its fourth tone it means daddy (ba4ba  ). By the way there is no tone mark above the second ba for "daddy" as it is soft and brief and has what is called a "neutral" tone. ). By the way there is no tone mark above the second ba for "daddy" as it is soft and brief and has what is called a "neutral" tone.
The word bai in the second tone i.e. bai2  means white, as in bai2 se4 (= white colour) means white, as in bai2 se4 (= white colour) 
On the other hand the same word bai in the third tone i.e. bai3  means a hundred. Thus 300 is san1 bai3 means a hundred. Thus 300 is san1 bai3 
Changing of Tones: 4-4 becomes 2-4The word of negation bu4 has the fourth tone so we say bu4 hao3  for "not good". However when two words that follow each other are both in the fourth tone as is the case with bu4 yao4 (don't want) then the first one changes to the second tone making it bu2 yao4 for "not good". However when two words that follow each other are both in the fourth tone as is the case with bu4 yao4 (don't want) then the first one changes to the second tone making it bu2 yao4  . Well this is what the rule says but to all intents and purposes you can stick to pronouncing bu in the fourth tone each time and it won't make much difference. Other examples are bu4 gou4 (not enough) converted to bu2 gou4 . Well this is what the rule says but to all intents and purposes you can stick to pronouncing bu in the fourth tone each time and it won't make much difference. Other examples are bu4 gou4 (not enough) converted to bu2 gou4  , bu4 bi4 (not necessary) converted to bu2 bi4 , bu4 bi4 (not necessary) converted to bu2 bi4  , and bu4 dui4 (not right i.e. wrong) converted to bu2 dui4 , and bu4 dui4 (not right i.e. wrong) converted to bu2 dui4  . If I were you I wouldn't worry unnecessarily about this rule and just pronounce them as bu4 yao4, bu4 gou4, bu4 bi4 or bu4 dui4 if it is easier for you that way. You will still be understood without any problem, have no doubts about that, and that is what's important! . If I were you I wouldn't worry unnecessarily about this rule and just pronounce them as bu4 yao4, bu4 gou4, bu4 bi4 or bu4 dui4 if it is easier for you that way. You will still be understood without any problem, have no doubts about that, and that is what's important!
More common Chinese words with the letter b follow. The Chinese word for stupid is ben4  ,
for hotel is bin1 guan3 ,
for hotel is bin1 guan3  , for a pen is
gang1 bi3 , for a pen is
gang1 bi3  , and for a museum is bo2 wu4 guan3 , and for a museum is bo2 wu4 guan3 
The next three words illustrate further how a change in the tone can change the whole sense of a word. But first let's see if you can give the four tones for bing (as we are going to make use of them below). If you need help with the first tone here it is 
And check your four tones with that in the audio file here 
Now let's take the word when it has the first tone: bing1 means ice and is the first word in bing1 qi2 lin2  which means ice-cream. which means ice-cream.
You need 2 Chinese words for one English word!When it has the third tone it means biscuit. Not really, because it cannot stand by itself. It needs a second word with it and together they mean biscuit. Thus the Chinese "word" for "biscuit" is actually two words: bing3 gan1  . .
This is something that you will notice more and more as you advance in your study of Chinese. There are indeed few Chinese words that can stand alone. Most of them come in pairs and have to be studied as such. In fact quite often there is not much point taking the two words apart and trying to make sense out of them individually. You just have to study both of them together as an entity, this being a case of "either you take us both together or you don't take us at all"! By the way, as I try to simplify matters wherever I can, I am not joining the two words together as many textbooks do. I think it is much easier for the learner to take in bing gan than binggan. When bing has got the fourth tone (bing4)  it means sick. it means sick.
If you ask someone not to do something the word to use is bie2 eg. "Don't smoke" is bie2 chou1 yan1  and "Don't be angry" is bie2 sheng1 qi4 and "Don't be angry" is bie2 sheng1 qi4  . .
So again two Chinese words or characters if you prefer (sheng1 qi4) are needed for the Chinese equivalent of "angry". But the same character bie2 in bie2 ren2  means "other" people. means "other" people.
More examples of two Chinese characters being needed to translate one English word are bang1 mang2  meaning "help" (both as a noun and as a verb) and shou2 biao3 meaning "help" (both as a noun and as a verb) and shou2 biao3  meaning a wristwatch. meaning a wristwatch.
Let's take another example with the word bao. When it has the first tone bao1 it means a bun. The steaming hot buns with stuffing inside that you can find all over China is called bao1 zi3 
When bao takes on the third tone (bao3) it means to have eaten one's fill or be full. Thus if you are at a dinner and your host insists that you eat some more you could politely refuse by saying bao3 le  (I am full or repleted) (I am full or repleted)
When bao takes on the fourth tone i.e. bao4 it means to report - but here again it has to be used with another word (remember what I said earlier). Thus the verb "to report" (give an account of something) is actually bao4 gao4  while the Chinese word for a newspaper is bao4 zhi3 while the Chinese word for a newspaper is bao4 zhi3  . So get used to the fact that very often in Chinese one English word is represented by not one but two Chinese characters together as a pair. . So get used to the fact that very often in Chinese one English word is represented by not one but two Chinese characters together as a pair.
Transliterated names
By the way foreign names are often translated (or rather transliterated) into Chinese by giving them their approximative Chinese sound eg. Paris is ba1 li2  , Rome is luo2 ma3 , Rome is luo2 ma3  , London is lun2 dun1 , London is lun2 dun1  and New York is niu3 yue1. and New York is niu3 yue1. 
However the Chinese name for McDonald's (mai4 dang1 lao2)  is nowhere near its English pronunciation. This is because when McDonald's first came to Hong Kong in 1975 it was called Mak dang lo in Cantonese and the Mandarin name is derived from the Cantonese name instead of the American. In fact McDonald's only came to mainland China in 1990 in the city of Shenzhen (and in Beijing in 1992). is nowhere near its English pronunciation. This is because when McDonald's first came to Hong Kong in 1975 it was called Mak dang lo in Cantonese and the Mandarin name is derived from the Cantonese name instead of the American. In fact McDonald's only came to mainland China in 1990 in the city of Shenzhen (and in Beijing in 1992).
More vocabulary (words starting with b)To go to work or be at work is shang4 ban1  but when ban takes the fourth tone (ban4) then it means half, as in yi2 ban4 but when ban takes the fourth tone (ban4) then it means half, as in yi2 ban4  meaning (one) half of something*. meaning (one) half of something*.
I might (or might not) have already introduced the two very important adjectives in any language and that is "small" (xiao3) and da4 (pronounced as the tar in tarte) meaning "big" in Chinese. Anyway I am going to mention these two words here as they are used to express two of the fundamental needs of every human being (and even animals). Can you guess what they are? I don't think you can as almost everybody is likely to come up with "eat" or "drink" or "sleep" but not what I am thinking of. Of course these three are fundamental needs (and there are more than a dozen of them surely). But the two fundamental needs of mankind that I am bringing up here have to do with emptying what we have eaten or drunk (in order to be able to eat and drink again!). But the Chinese (like the Malays I think) consider that to pee is a "small" thing while to defecate is a "big" thing. While on this subject I cannot help mentioning that Malaysians jocularly refer to these two actions as "putting out the fire" and "going to the bank to deposit some money". I don't think I need to tell you which is which! So to cut a long story short (sorry, longwindedness is one of my vices) xiao3 bian4  means "to urinate". The opposite of this (to defecate) is simply da4 bian4. Don't try to translate them! It's easier to remember them as "small pian" and "big pian"! Didn't I say that I will try to make the study of pinyin easier for you? means "to urinate". The opposite of this (to defecate) is simply da4 bian4. Don't try to translate them! It's easier to remember them as "small pian" and "big pian"! Didn't I say that I will try to make the study of pinyin easier for you?
Incidentally the word bian when it is used in the 1st tone (instead of the 4th as above) means "side". Thus zuo3 bian1  means the "left side" while yu4 bian1 means the right side (of a street, etc.) I always find it confusing to learn both left and right at the same time so if I were you I would just commit to memory only one of the two directions right now - doesn't really matter if it's left or if it's right. The other can come in later as the main thing is to be very clear with one direction from the very beginning (so you won't get confused with the other direction later on). means the "left side" while yu4 bian1 means the right side (of a street, etc.) I always find it confusing to learn both left and right at the same time so if I were you I would just commit to memory only one of the two directions right now - doesn't really matter if it's left or if it's right. The other can come in later as the main thing is to be very clear with one direction from the very beginning (so you won't get confused with the other direction later on).
With all these examples I think by now you should be used to pronouncing the b in pinyin as p and not as b! To end this lesson let's revise the four tones, shall we? See if you can give the four tones for mao. Do you need help with the first tone to start you off? Here it is: mao1  . Check your pronunciation of the four tones for mao here . Check your pronunciation of the four tones for mao here  . .
By the way mao1 means a cat so if you have a cat you might start naming your cat Mao to help you to remember instead of Luna or Nala! But make sure you pronounce it with the first tone. This is because if you pronounce it with the second tone (mao2) it means body hair or fur so if your cat has plenty of fur you can say wo3 de4 mao1 you2 hen3 duo1 mao2  (= My cat has a lot of fur). (= My cat has a lot of fur).
And if you pronounce it with the fourth tone (mao4) then it means a hat (more specifically a hat is mao4 zi3)  . .
Summary of Section 2 (with Chinese characters)
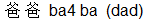

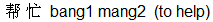
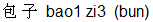


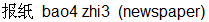
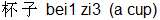


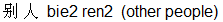
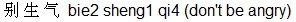
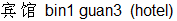
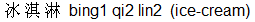




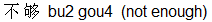



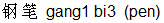

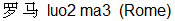
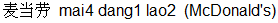




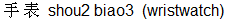




|
| Back to Section 1 | On to Section 3 |